
Pair that with the in-program use of the git version control system, and you have yourself an all-around go-to program for your developers to work on. Visual Studio Code as a code editor brings a lot of useful features for developers of all kinds.
You would need to to download and install GCM.Efficiency, simplicity, and team collaboration capabilities are some of the most in-demand qualities, in the modern working environment. If you get, on Linux: git: 'credential-manager-core' is not a git command. Visual Studio Code will use that credential helper, with the new "password" (token) stored for the remote site. (replace credential-manager-core by credential-manager if the credential helper is manager instead of manager-core) Then git credential-manager-core store to store the token: printf "protocol=https\nhost=\nusername=\npassword="|git credential-manager-core store (a git credential-manager-core get would read that old value) printf "protocol=https\nhost=\nusername="|git credential-manager-core erase ("destructive command" in that it will remote the entry and its associated value, the password) If it is manager or manager-core, remove the old password with a git credential-manager-core erase If you are using HTTPS URLs for your remote repositories, that means you can cache your credentials: today, that would be your GitHub user account name and password, tomorrow, the password will be your token.Ĭheck your git config credential.helper result.
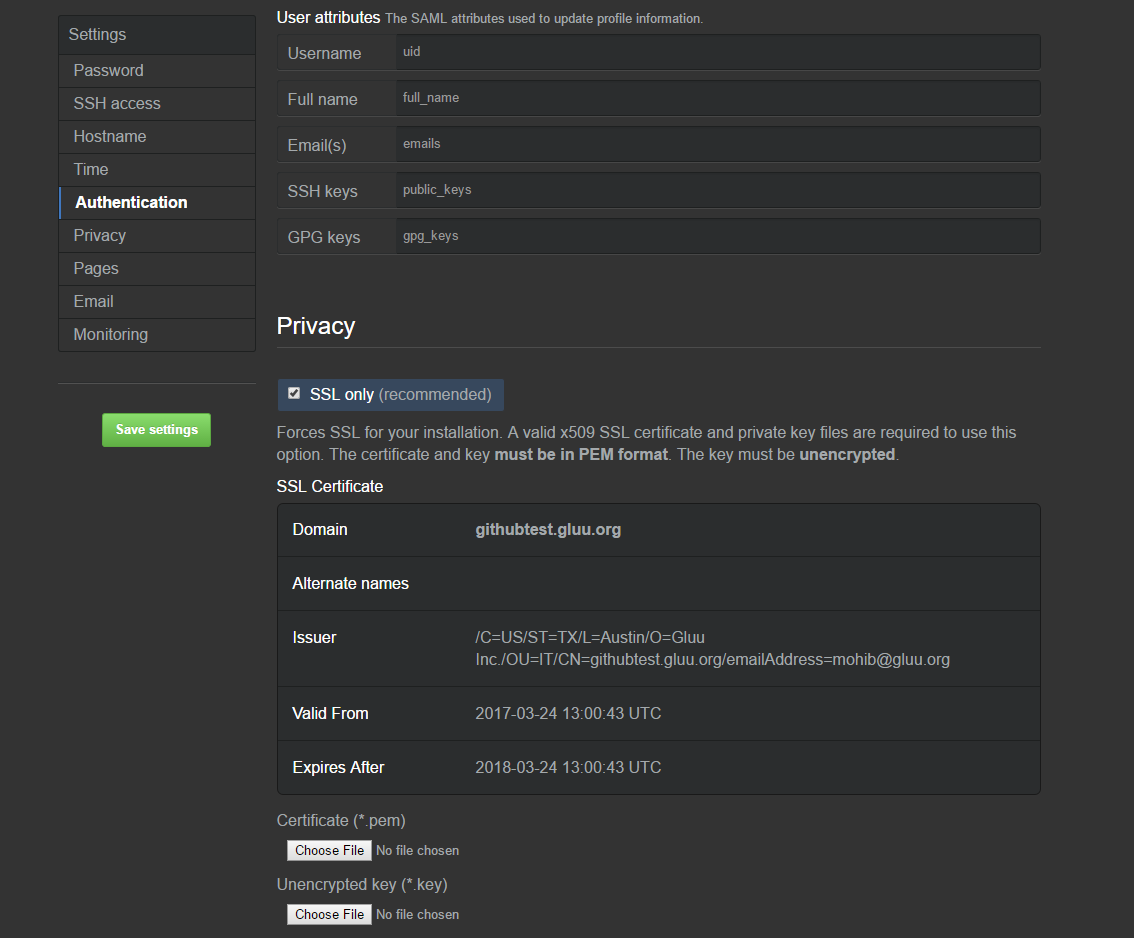
origin (fetch)Īlso after setting git remote set-url origin git remote -v should be something like: origin (fetch) You can type git remote -v to see your origin or upstream. When generating a personal access token, make sure to enable workflow:



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
